Remote Access
This guide serves two purposes:
1. To explain how to configure a workstation to operate as a RAS server. Here, the term workstation means any computer on a TCP/IP network that:
![]() is running NT 4.0 or NT 3.51, and
is running NT 4.0 or NT 3.51, and
![]() is not an AspeNet Server.
is not an AspeNet Server.
2. To explain how to configure a remote computer to operate as a RAS client. Here, the term remote computer means any computer not connected to a LAN that is running Windows 95, Windows NT 4.0, or Windows NT 3.51.
RAS stands for Remote Access Service.
Any workstation running Windows NT 4.0, or Windows NT 3.51 can be configured as a RAS Server, even if the workstation is used as an AspeNet workstation.
Any computer running Windows 95, Windows NT 4.0, or Windows NT 3.51 can be configured to run as a RAS Client.
Setting up a RAS Server on an workstation allows you to dial into the workstation from a RAS Client and run AspeNet workstation software. This is possible because the RAS Server operates as though it were a network router, taking information from an AspeNet Server across a network and piping it through the RAS Server’s modem to a RAS Client.
Remote Access Service for Windows NT lets you connect to your office network from a remote site, such as your home, a hotel, or anywhere there is an outlet for your computer and phone jack for your modem. Once you have connected, Remote Access lets you work with all your applications as though you were physically in the office, directly connected to the physical network.
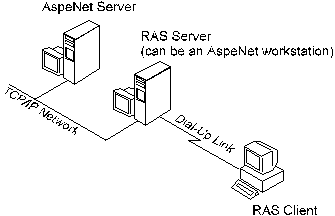
After connecting, the telephone link is transparent. That is, you can access and view network resources in the same way as your office colleagues who are working on computers physically connected to the LAN.